As you may know, the ribbon blender is a highly efficient mixing equipment primarily used for mixing powders with powders, or for mixing a large proportion of powder with a small amount of liquid.
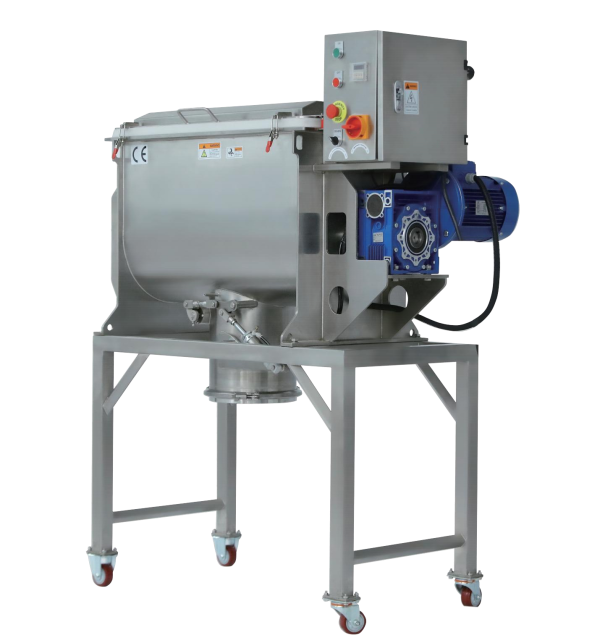

Compared to other horizontal blenders, such as paddle blenders, the ribbon blender has a larger effective mixing area, but it does cause some degree of damage to the material form. This is because the gap between the ribbon blades and the mixing trough wall is small, and the force from the ribbons and the wall of the mixing trough can crush the material and generate heat, which may affect the properties of some materials.
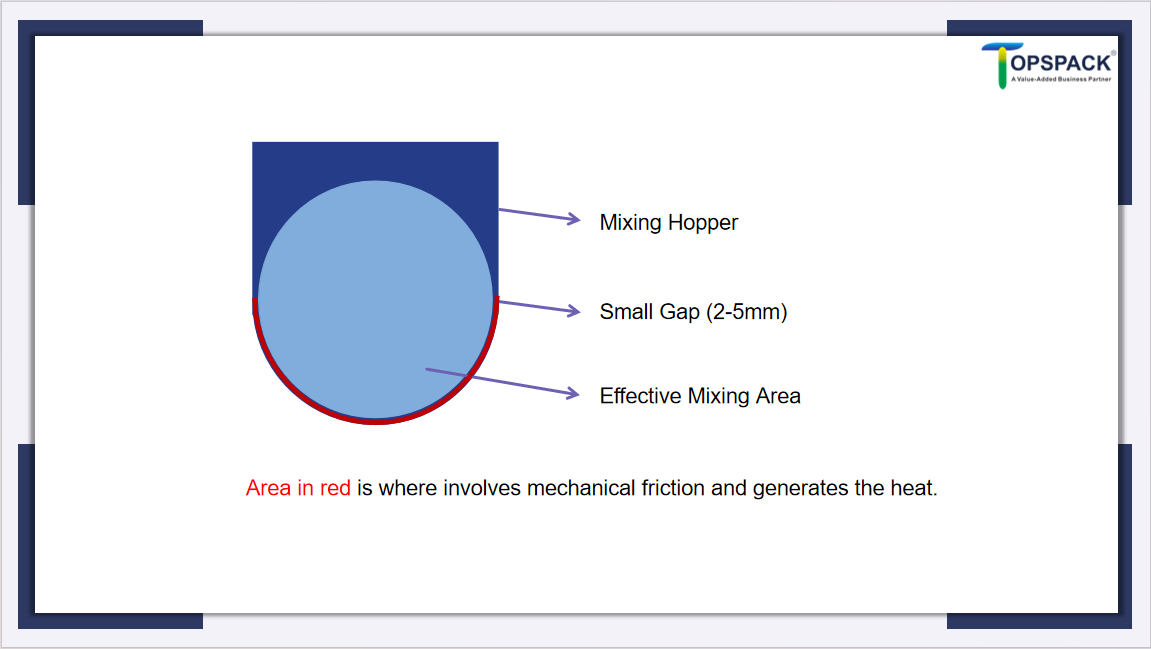
When selecting a ribbon blender, I can consider the following aspects:
- Material form: The material should be in powder or small granular form, and at least the damage to the material form should be acceptable.
- Heat generated by friction between material and machine: Whether the heat generated affects the performance and properties of specific materials.
- Simple calculation of blender size: Calculate the required size of the ribbon blender based on material needs.
- Optional configurations: Such as material contact parts, spray systems, cooling or heating mediums, mechanical seals, or gas seals.
After checking the material form, the next concern is the heating problem.
What should we do if the material is temperature-sensitive?
Some powders in the food or chemical industries need to remain at lower temperatures. Excessive heat can cause changes in the physical or chemical properties of the material.
Let’s use a limit of 50°C as an example. When raw materials enter the blender at room temperature (30°C), the blender may generate heat during operation. In certain friction zones, the heat could cause the temperature to exceed 50°C, which we want to avoid.

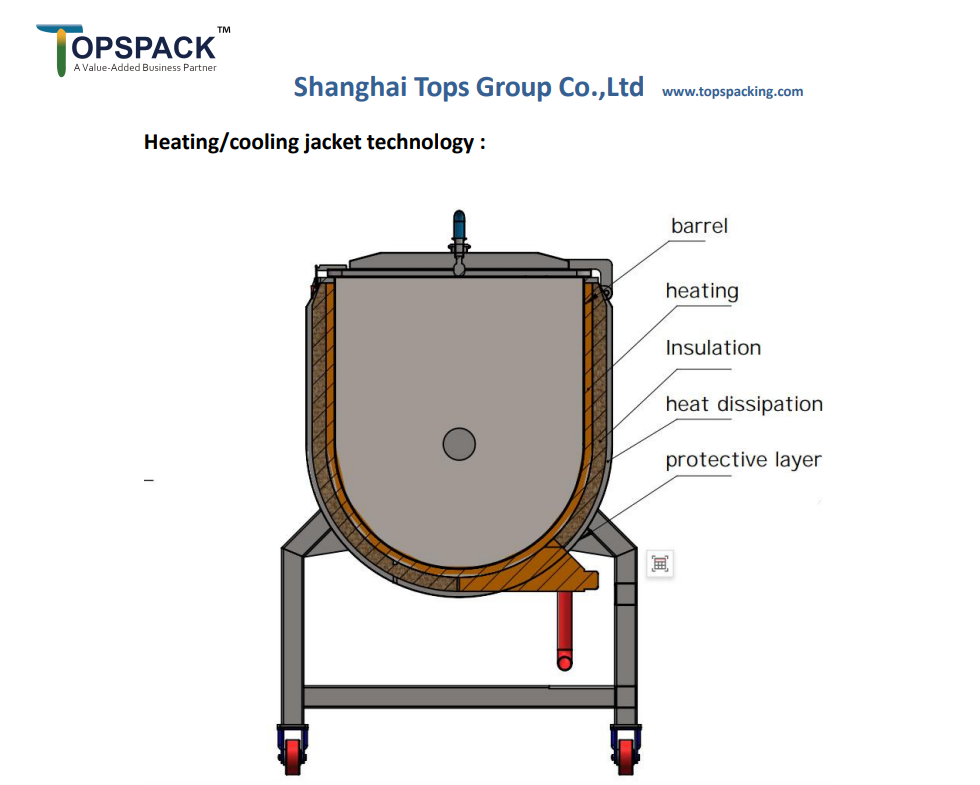
To solve this, we can use a cooling jacket, which uses room temperature water as the cooling medium. The heat exchange between the water and the friction from the mixing walls will cool the material directly. In addition to cooling, the jacket system can also be used for heating the material during mixing, but the inlet and outlet of the heat medium need to be changed accordingly.
For cooling or heating, a temperature gap of at least 20°C is necessary. If I need to control the temperature further, sometimes a refrigeration unit for cooling medium water may be useful. Additionally, there are other mediums, such as hot steam or oil, that can be used for heating.
How to calculate the ribbon blender size?
After considering the heating problem, here is a simple method to select the ribbon blender size, assuming:
The recipe is 80% protein powder, 15% cocoa powder, and 5% other additives, with a required output of 1000kg per hour.
1.The data I need before the calculation.
| Name | Data | Note |
| Requirement | How many A Kg per Hour? | How long for each time depends. B Times per Hour
For large size like 2000L, one hour for 2 times. It depends the size. |
| 1000 Kg per Hour | 2 times per Hour | |
| Capability | How many C Kg each Time? | A Kg per Hour÷ B Times per Hour=C Kg each Time |
| 500 Kg each Time | 1000 Kg per Hour÷2 times per Hour= 500 Kg each Time | |
| Density | How many D Kg per Liter? | You can search the main material in google or use a 1L container to measure net weight. |
| 0.5 Kg per Liter | Take the protein powder as the main material.
In google it is 0.5 grams per cubic milliliter= 0.5 Kg per Liter. |
2.The calculation.
| Name | Data | Note |
| Loading volume | How many E Liter each time? | C Kg each Time ÷D Kg per Liter
=E Liter each time |
| 1000 Liter each time | 500 Kg each Time÷ 0.5 Kg per Liter
=1000 Liter each time |
|
| Loading rate | Max 70% of Total Volume | Best mixing effect for ribbon blender |
| 40-70% | ||
| Min Total volume | How many F Total volume at least? | F Total volume×70%
=E Liter each time |
| 1430 Liter each time | 1000 Liter each time÷70%
≈1430 Liter each time |
The most important data points are the Output (A kg per hour) and Density (D kg per liter). Once I have this information, the next step is to calculate the total volume required for a 1500L ribbon blender.
Optional configurations to consider:
Now, let's explore other optional configurations. The main consideration is how I want to mix my materials in the ribbon blender.
Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel 304, Stainless Steel 316: What material should the ribbon blender be made from?
This depends on the industry in which the blender is being used. Here is a general guide:
|
Industrial |
Material of blender |
Example |
|
Agriculture or chemical |
Carbon steel |
Fertilizer |
|
Food |
Stainless steel 304 |
Protein powder |
|
Pharmaceutical |
Stainless steel 316/316L |
Chlorine-containing disinfectant powder |
Spray System: Do I need to add liquid while mixing?
If I need to add liquid to my mixture or use liquid to help with the blending process, then a spray system is necessary. There are two main types of spray systems:
- One that uses clean compressed air.
- Another that uses a pump as the power source, which is capable of handling more complex situations.
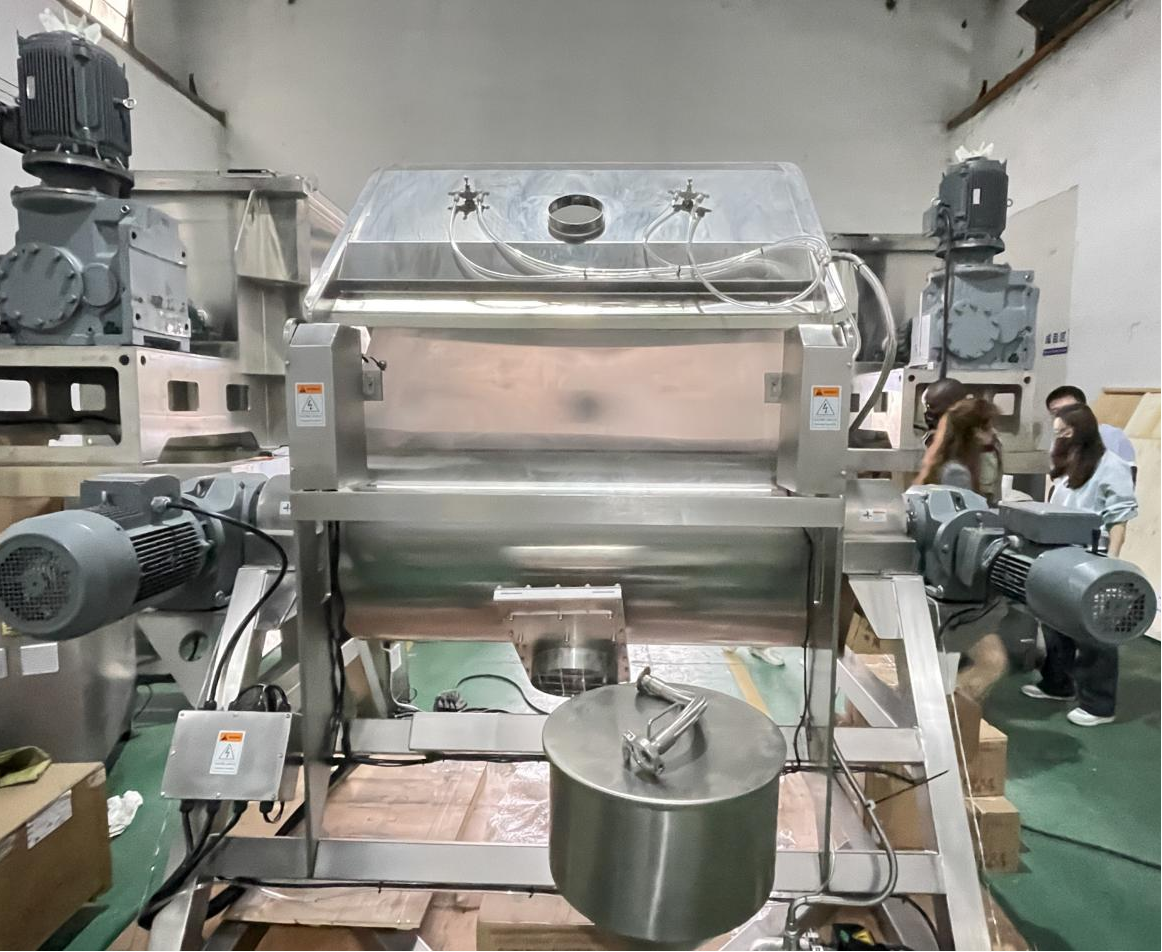

Packing Sealing, Gas Sealing and Mechanical Sealing: Which is the best choice for shaft sealing in a blender?
- Packing seals are a traditional and cost-effective sealing method, suitable for moderate pressure and speed applications. They use soft packing materials compressed around the shaft to reduce leakage, making them easy to maintain and replace. However, they may require periodic adjustment and replacement over extended periods of operation.
- Gas seals, on the other hand, achieve sealing without contact by forming a gas film using high-pressure gas. The gas enters the gap between the wall of the blender and the shaft, preventing leakage of the sealed medium (such as powder, liquid, or gas).
- Composite mechanical seal offers excellent sealing performance with easy replacement of wear parts. It combines mechanical and gas sealing, ensuring minimal leakage and extended durability. Some designs also include water cooling to regulate temperature, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
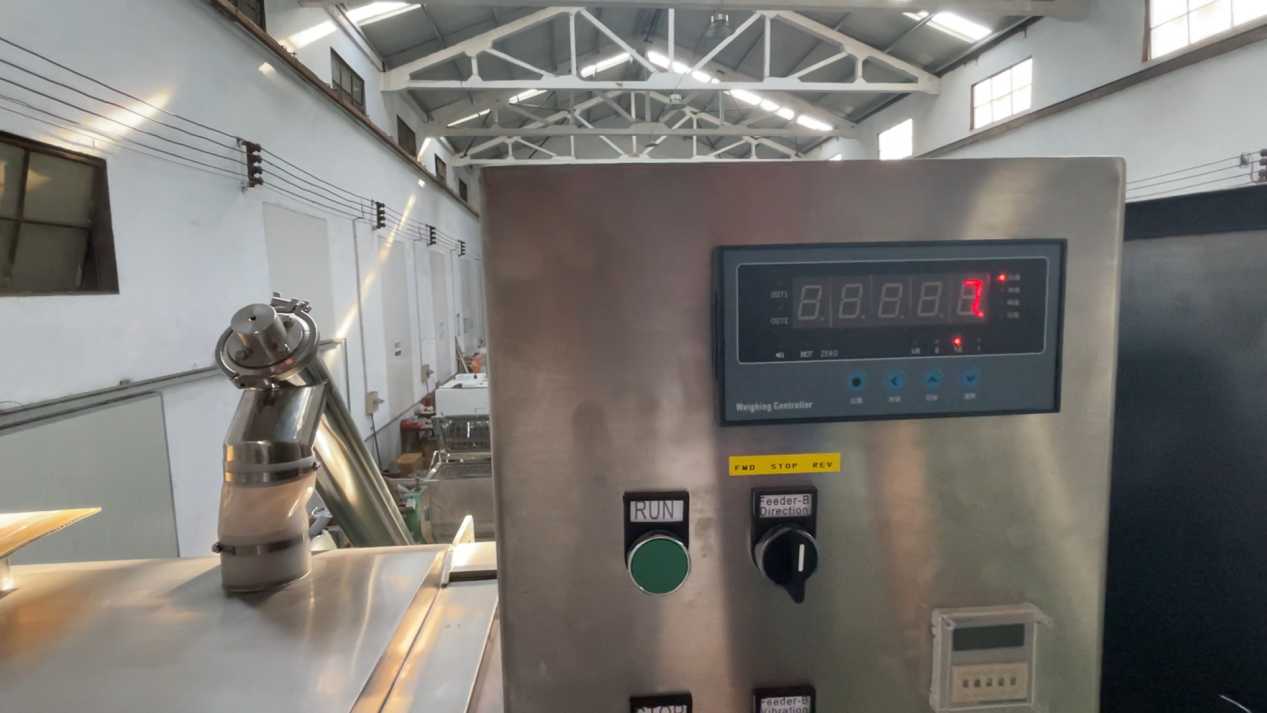
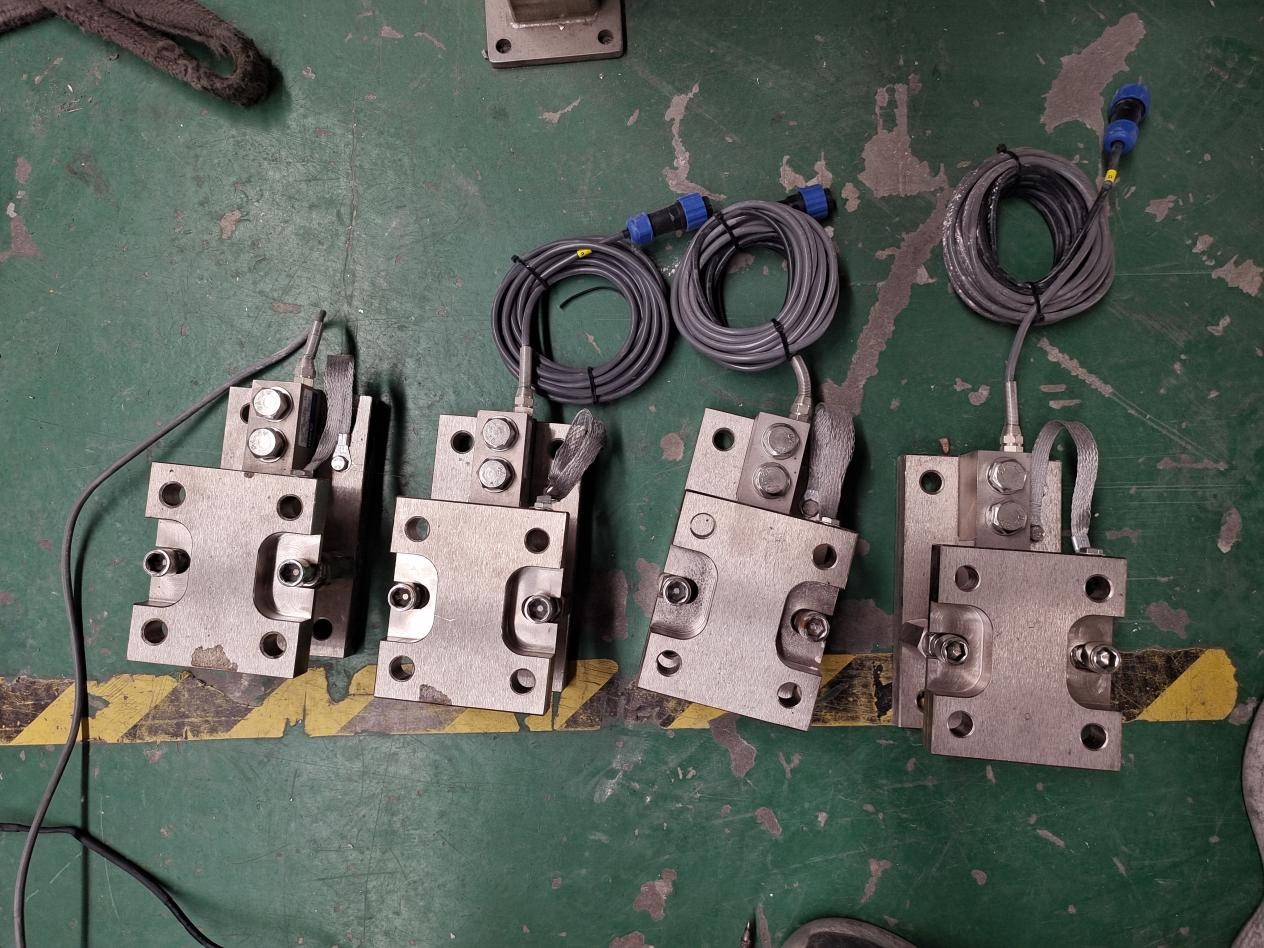
Weighing System Integration:
A weighing system can be added to the blender to accurately measure each ingredient’s proportion during the feeding process. This ensures precise formulation control, improves batch consistency, and reduces material waste. It is especially useful in industries requiring strict recipe accuracy, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.


Discharge Port Options:
The discharge port of a blender is a critical component, and it typically features several valve types: butterfly valve, flip-flop valve, and slide valve. Both the butterfly and flip-flop valves are available in pneumatic and manual versions, offering flexibility depending on the application and operational requirements. Pneumatic valves are ideal for automated processes, providing precise control, while manual valves are more suited for simpler operations. Each valve type is designed to ensure smooth and controlled material discharge, minimizing the risk of clogs and optimizing efficiency.

If you have any further questions about the principle of the ribbon blender, feel free to contact us for more consultation. Leave your contact information, and we will reach out to you within 24 hours to provide answers and assistance.
Post time: Feb-26-2025
