Tip: Please note that the paddle mixer mentioned in this article refers to a single-shaft design.
In industrial mixing, both paddle mixers and ribbon blenders are commonly employed for a wide range of applications. While both machines perform similar tasks, they have distinct designs and capabilities tailored to specific material properties and mixing needs.
Ribbon blenders are typically more efficient for standard powder blending and large-scale operations, offering high-volume mixing capabilities. On the other hand, paddle mixers are better suited for more delicate materials, heavy or sticky substances, or complex formulations with multiple ingredients and significant variations in density. By understanding the material type, required batch size, and specific mixing goals, companies can select the most appropriate mixer to ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Here’s a comprehensive comparison between the two types of mixers, examining their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for different applications:
| Factor | Single Shaft Paddle Mixer | Ribbon Blender |
| Batch SizeFlexibility
|
Works efficiently with fill levels between 25-100%. | Requires a fill level of 60-100%for optimal blending. |
| Mix Time | Typically takes 1-2 minutes for dry material blending. | Dry mixing usually takes around 5-6 minutes. |
| ProductCharacteristics
|
Ensures even mix+of materials with varying particle sizes,shapes, and densities,preventing segregation. | Longer mixing times are necessary to handle ingredients of varying sizes,shapes,and densities,which could lead to segregation. |
| High Angle ofRepose
|
Ideal for materials with a high angle of repose. | Extended mixing times may lead to segregation with such materials. |
| Shear/Heat(Friability)
|
Provides minimal shear, reducing the risk of product damage. | Applies moderate shear, which may require additional time to achieve uniformity. |
| Liquid Addition | Efficiently brings materials to the surface for quick liquid application. | Requires more time to add liquid without forming clumps. |
| Mix Quality | Delivers mixes with low standard deviation (≤0.5%)and coefficient of variation(≤5%)for a 0.25 lb sample. | Typically results in a 5% standard deviation and 10% coefficient of variation with a 0.5 lb sample. |
| Filling/Loading | Can handle random loading of materials. | For efficiency, it’s recommended to load ingredients closer to the center. |
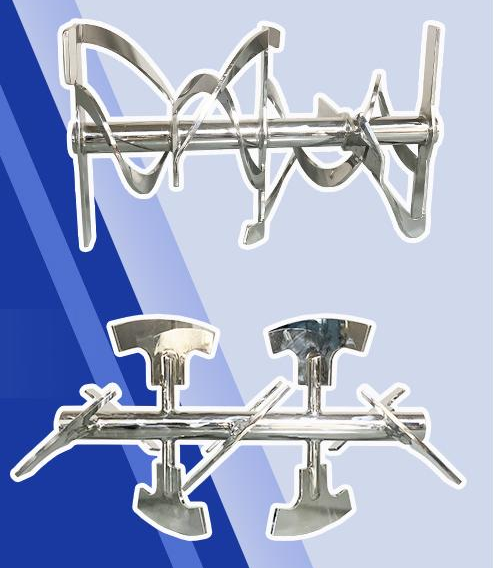
1. Design and Mixing Mechanism
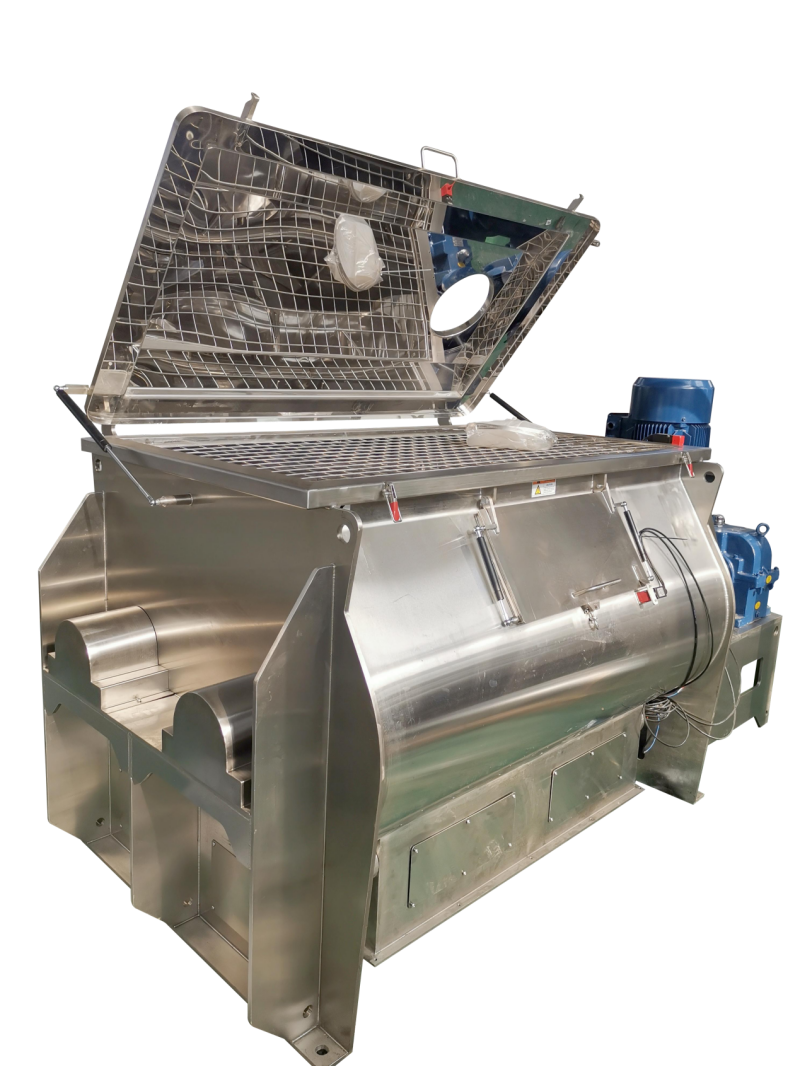
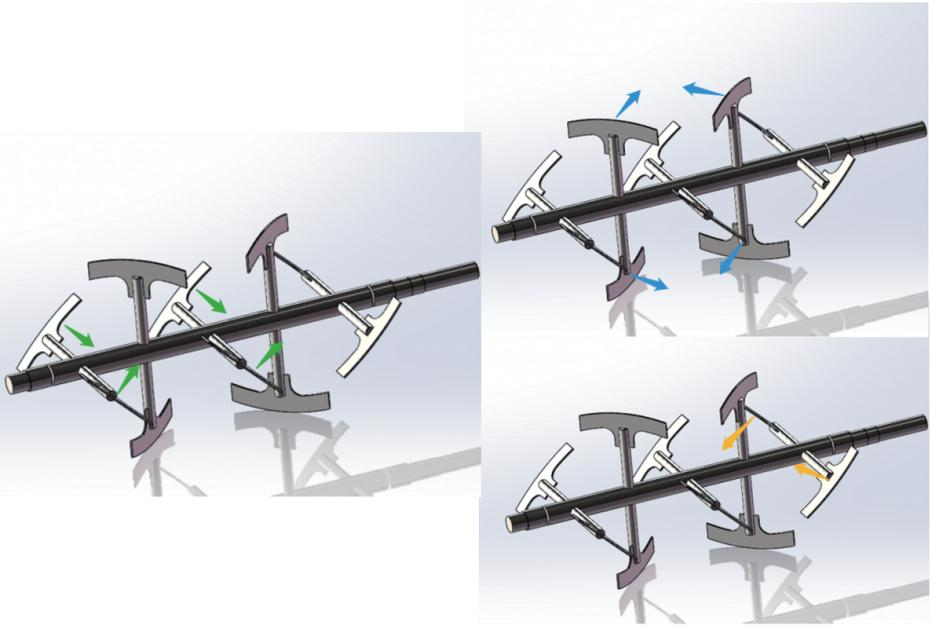
The paddle mixer features paddle-shaped blades mounted on a central shaft. As the blades rotate, they gently agitate the material within the mixing chamber. This design makes paddle mixers ideal for materials that require a more delicate mixing process, as the shear force applied is minimal.
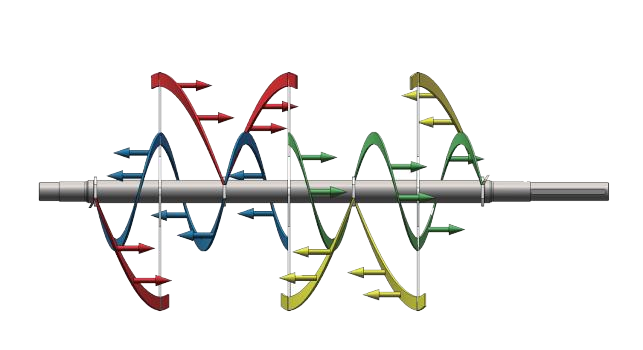
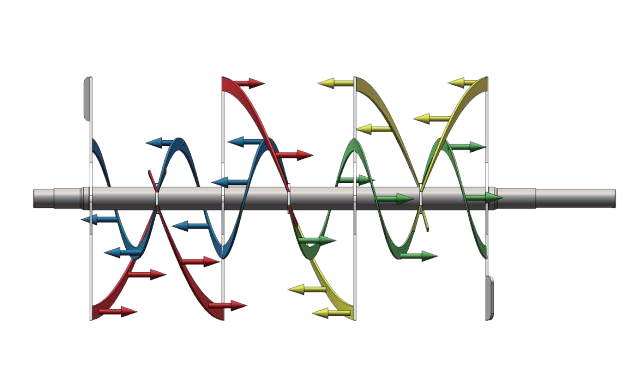
In contrast, the ribbon blender uses two ribbons that rotate in opposite directions. The inner ribbon pushes the material from the center toward the outer walls, while the outer ribbon moves it back toward the center. This action ensures more efficient and uniform blending, particularly for powder-based materials, and is preferred for achieving a homogeneous mixture.
2. Mixing Efficiency and Speed
Both mixers are designed to achieve uniform blends, but ribbon blenders excel when handling dry powders and materials requiring thorough mixing. The dual, counter-rotating ribbons move materials quickly, promoting a consistent and homogeneous blend. Ribbon blenders are more efficient in terms of mixing speed, making them ideal for both small and large batch sizes.
On the other hand, paddle mixers mix at a slower pace but are better suited for denser and more robust materials. These mixers are particularly effective for handling heavy, sticky, or cohesive substances, as their slower mixing action ensures thorough blending without damaging the material.
3. Material Compatibility
Both mixers are versatile, but each has distinct strengths depending on the material type. Paddle mixers are ideal for delicate, heavy, sticky, or cohesive substances, such as wet granules, slurries, and pastes. They are also effective for blending complex formulations with multiple ingredients or those with significant density differences. The gentle mixing action of the paddles helps preserve the integrity of the material. However, paddle mixers can generate more dust during operation, which may be problematic in certain settings.
In contrast, ribbon blenders are particularly effective for mixing fine powders or powder-liquid combinations. They are commonly used in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, where achieving a uniform, homogeneous mix is crucial. The counter-rotating ribbons efficiently blend materials with similar densities, ensuring consistent results in less time. Ribbon blenders are better suited for large-scale mixing and standard powder applications.
|
Application Examples |
||
|
Application |
Single Shaft Paddle Mixer |
Ribbon Blender |
|
Biscuit Mix |
Ideal. Solid fat or lard remains in chunks, with minimal shear applied. |
Not suitable. Ribbon blenders may break down delicate ingredients. |
|
Breading Mix |
Ideal. Effective for ingredients with varying sizes and densities, with minimal shear. |
Suitable. Ribbon blenders effectively mix particles and liquids but may cause breakage. |
|
Coffee Beans (Green or Roasted) |
Ideal. Preserves the integrity of the beans with minimal shear. |
Not suitable. Ribbon blenders may damage the beans during mixing. |
|
Flavored Drink Mix |
Not recommended. Shear is necessary for even powder dispersion. |
Suitable. Shear helps disperse powders for a homogeneous blend of sugar, flavor, and color. |
|
Pancake Mix |
Ideal. Works well, especially when mixing a variety of ingredients. |
Suitable. Ensures smooth blending, particularly with fats. Shear is required. |
|
Protein Drink Mix |
Ideal. Suitable for mixing ingredients of varying densities with minimal shear. |
Not recommended. Ribbon blenders may overwork delicate proteins. |
|
Seasoning/Spice Blend |
Ideal. Handles variations in size and shape, with minimal shear. |
Suitable. Works well when liquids like oils are added, providing good dispersion. |
|
Sugar, Flavor, and Colorant Mix |
Ideal for keeping intact pieces like nuts or dried fruits, with minimal shear. |
Not recommended. Ribbon blenders may cause breakage or excessive mixing. |
4. Size and Capacity
Ribbon blenders are generally better suited for handling large volumes. Their design allows for efficient processing of bulk materials, making them ideal for high-capacity production needs. Ribbon blenders typically offer higher throughput and are more suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
On the other hand, paddle mixers are more compact, making them a good choice for smaller batch sizes or more flexible, versatile operations. While they may not handle large volumes as efficiently as ribbon blenders, paddle mixers excel in providing a more uniform blend in smaller batches, where precision is key.
5. Energy Consumption
Ribbon blenders typically require more energy due to their design complexity and the rapid mixing action. The counter-rotating ribbons generate substantial torque and shear forces, which demand more power to sustain the desired mixing speed, particularly in larger batches.
In contrast, paddle mixers are generally more energy-efficient. Their simpler design and slower mixing speed result in lower energy consumption, making them a better choice for applications where high-speed mixing is not a priority.
6. Maintenance and Durability
Both ribbon blenders and paddle mixers require routine maintenance, but the ribbon blender’s more intricate design can make it harder to maintain. The ribbons are subject to wear, especially when processing abrasive materials, and may need more frequent checks and replacements. Despite this, ribbon blenders are known for their durability, making them well-suited for continuous operation in demanding settings.
On the other hand, paddle mixers feature a simpler design with fewer moving parts, which typically reduces the need for frequent maintenance. They are easier to service but may not be as durable when dealing with particularly abrasive or harsh materials.
7. Cost
Generally, the cost of a ribbon blender is comparable to that of a paddle mixer. Despite the more complex design of the ribbon blender with its counter-rotating ribbons, the pricing is often similar across most manufacturers. The decision to choose between the two mixers is usually driven more by the specific requirements of the application rather than cost.
Paddle mixers, with their simpler design, may offer some savings in certain scenarios, but the cost difference is usually minimal when compared to ribbon blenders. Both mixers are economically viable options for smaller operations or less demanding mixing tasks.
8. Double Shaft Paddle Mixer
The double shaft paddle mixer is equipped with two rotating shafts that offer four operation modes: same direction rotation, opposite direction rotation, counter-rotation, and relative rotation. This flexibility enables highly efficient and customized mixing for various materials.
Known for its superior performance, the double shaft paddle mixer achieves up to twice the mixing speed of both ribbon blenders and single shaft paddle mixers. It is especially effective for handling sticky, coarse, or wet materials, making it ideal for industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
However, this advanced mixing capability comes at a higher cost. Double shaft paddle mixers are typically more expensive than ribbon blenders and single shaft models. The price is justified by their increased efficiency and versatility in handling more complex materials, making them a great fit for medium- to large-scale operations.
If you have any additional questions about the ribbon blender’s principles, don’t hesitate to reach out to us for expert advice. Simply provide your contact details, and we will get back to you within 24 hours to help address any questions or concerns you might have.
Post time: Apr-16-2025